Spring energized seals
We kindly ask you to fill in our Questionnaire if you are interested in our products and would like to place an order for production. This will help to provide all the necessary information and save the time.

The development of equipment for oil production from deep horizons at elevated pressures, temperatures, aggressiveness of accompanying media, gas liquefaction, drilling in high latitudes, shale oil and gas production requires the use of new technological solutions, including sealing units. At the same time the actual problems in the creation of new samples of sealing equipment are the increase of their reliability at high operating parameters and reduction of mass and dimensional characteristics of units.
Along with rings and cups, oil seals are one of the main types of contact seals combining small dimensions with high performance characteristics. They are mostly used in sealing of movable joints in reciprocating and rotating couples as well as in critical fixed joints. Depending on working pressures, sealed media, speeds of mutual displacement, different types of oil seals are used, differing in design and materials of which they are made. One of the types of sealing cuffs, which, despite their excellent characteristics, are still little used in domestic engineering, are polymer spring energized seals (SES).
Spring energized seals are widely used for sealing in the most critical assemblies. They are applied in space and nuclear engineering, cryogenic engineering, in mechanical engineering for oil and gas industry. The seal consists of a shell (the seal itself) made of various polymeric or composite materials and a springing element representing various types of springs or rubber rings. They have the advantage of providing a constant initial contact pressure by the spring or O-ring and providing a self-sealing effect when external pressure is applied to the seal. Nowadays our company is implementing the import substitution program and can offer our customers its own versions of this combined seal both with the use of various metal springs and a patented design with an encapsulated ring as a spring element, providing unique chemical resistance. The seals are manufactured according to TS 22.29.29-033-34724672-2018.
The configuration of the seal edges can also vary and depends on the purpose and function of the seal and the design of the sealing unit. It can be combined with a dirt-removing function, in which case the seal edges are made with sharp edges to retain dirt - the sharp edge on the cuff ends acts as a scraper to protect against abrasive particles. Elongated seals are applied for high pressures to reduce the possibility of extrusion into the gap. Studies have shown that the best performance is obtained with seals of two types of lobes, the shape of which is primarily determined by the type of spring.
Materials used for manufacturing of sleeves: fluoroplastic, filled fluoroplastic (PTFE), polyetheretherketone (PEEK), ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, polyurethane, polyamide.
| Material | Resistance in aggressive media | Wear resistance | Heat resistance, ºС | Dry sliding friction coefficient | Max. pressure, MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluoroplastic | + | - | 200 | 0,08 | 20 |
| Fluoroplastic reinforced | + | ± | 220 | 0,1 | 30 |
| Ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene | + | + | 100 | 0,1 | 50 |
| Polyetheretherketone | + | + | 260 | 0,15 | 100 |
| Polyamide | ± | + | 170 | 0,15 | 70 |
| Polyurethane | - | + | 80 | 0,25 | 40 |
Spring element: flat or round springs made of stainless steel, elastomeric O-rings or fluoroplastic rubber ring (RFR). Additionally other kinds, types, materials of springs can be offered if required.
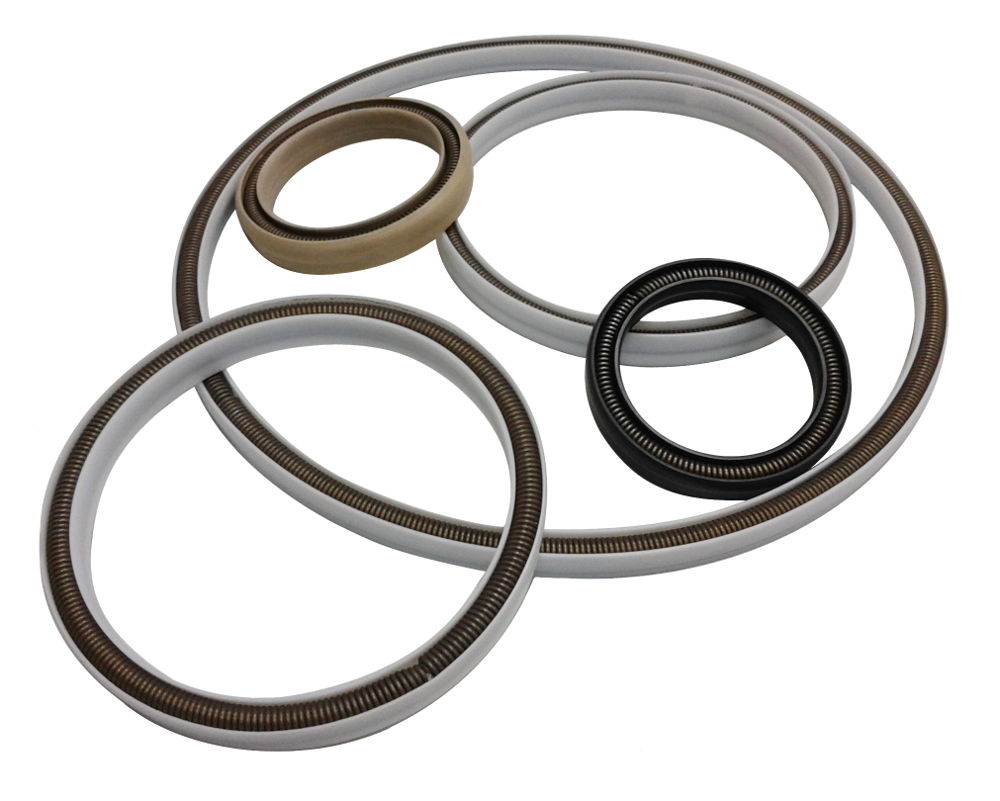
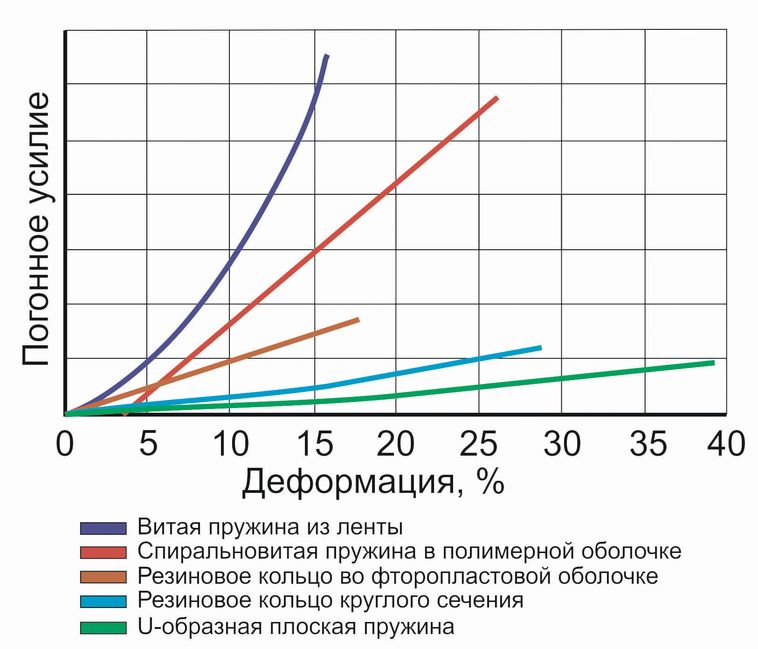
It is obvious that, like with all contact seals, the fundamental dependence of the linear force on the compression strain of the seal, i.e. the force arising from the transverse compression of the seal when it is inserted into the groove, related to the unit length of the seal perimeter, will be fundamental. The figure shows the dependencies for different spring elements. It can be observed that seals with various spring elements have different compression strain dependencies and this must be carefully weighed when selecting a seal. For example, an increase in driving force certainly improves leak tightness, but increases friction and seal wear in movable joints. In stationary seals high linear forces can lead to increased creep under load with loss of tightness. It is therefore possible to select spring elements with different characteristics to provide higher or lower forces.
In order to prevent extrusion of the seal material into the gap at high pressures, seals are manufactured with an extended shank and protective rings are used. Spring energized seals (SES) can be used without protective rings up to 60 MPa, at higher pressures the groove dimensions should provide for the installation of protective rings. It is also recommended to use protective rings when high pressures and temperatures are combined. Specific recommendations can be given when considering the sealing unit.
Application benefits
- Operating temperature from -150 to +250ºС
- Pressure up to 100 MPa
- Decompression resistance and unique chemical resistance
- Aging and hydrolysis resistance
- High wear resistance
- Low friction coefficient (0.09-0.11) and high sealing capacity from the lowest to the highest pressure levels by maintaining contact pressure with spring loaded elements.
- Absence of seals sticking when shutting down the equipment
- Operation with or without lubrication
Types of Spring energized seals
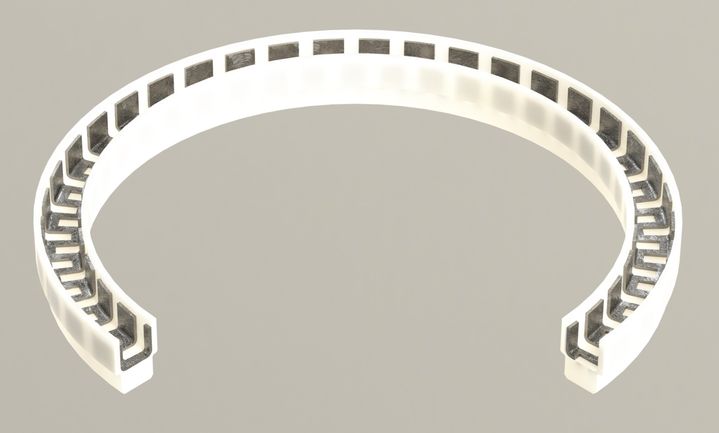
Types of seals.
Seal groove dimensions.
| Shaft diameter, mm (max.) | H, groove width, mm | L, groove length, mm |
|---|---|---|
| 6 до 180 | 2,3 | 3,6-6,2 |
| 6 до 250 | 3,05 | 4,8-7,7 |
| 13 до 300 | 4,75 | 7,1-10,8 |
| 50 до 500 | 6,1 | 9,5-14,7 |
| 50 до 1400 | 9,4 | 13,5-18 |
| 300 до 1400 | 12,7 | 18-23,5 |
Guidelines for cleanliness of sealing surfaces.
The highest possible hardness of the mating surfaces is advised.
| Media | Fixed packing | Sliding joint | Rotary seal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gases, low temperatures | Ra=0,3 μm | Ra=0,2 μm | Ra=0,1 μm |
| Low-viscosity media | Ra=0,6 μm | Ra=0,3 μm | Ra=0,2 μm |
| Water, oil and viscous liquid | Ra=0,8 μm | Ra=0,4 μm | Ra=0,2 μm |


 Назад
Назад