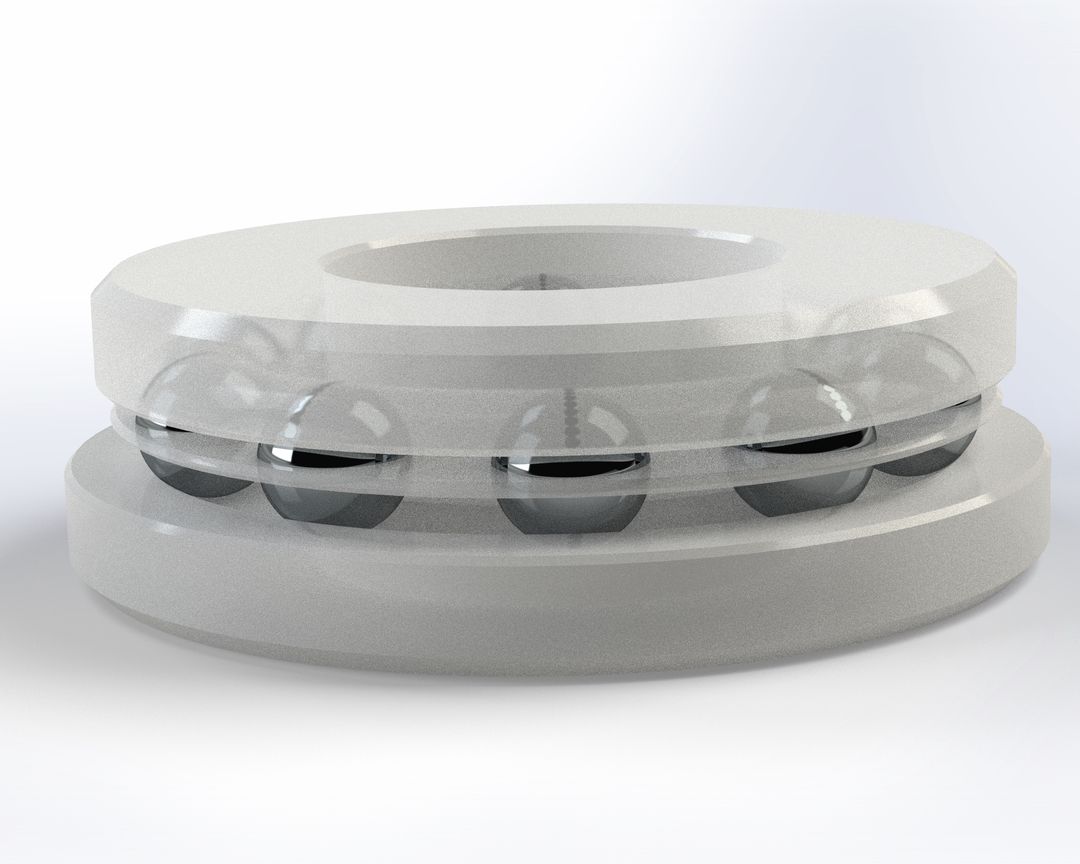
Rolling bearings

Polymer ball bearings are typically used in applications where resistance to moisture or chemicals is required. Steel cannot be used in these applications or has limited possibilities, which makes polymer ball bearings the best solution from both a technical and economic point of view.
Polymer ball bearings can be operated without lubrication. That is why they can also be applied where lubricants cannot be used, e.g. for hygienic reasons. The possible applications are as varied as the properties and advantages of polymer ball bearings. Please find below a partial list of the industries and applications where polymer ball bearings are already in use today:

- Medicine and pharmaceuticals
- Food industry
- Heating and air conditioning
- Chemical and electroplating industry
- Textile and pulp production
- Transport and material handling
- Electrical Engineering
- Measurement and Control
- Vacuum applications

Polymer ball bearings can be manufactured from a variety of materials and material combinations. The materials selected depend on the application. The properties of polymers differ significantly from steel. One of the most unique properties includes resistance to corrosion and chemicals.
Polymers used for bearings have a low coefficient of friction and have a high resistance to wear and fatigue. These self-lubricating bearings can run dry and do not require relubrication.
However, the loads and maximum speeds a polymer bearing can withstand are much lower than those of conventional all-metal bearings.
High specific strength (strength-to-weight ratio) is a valuable property of polymer bearings, especially where weight is an important design factor.
High dimensional stability over the entire service life is achieved due to the low creep tendency of polymers.
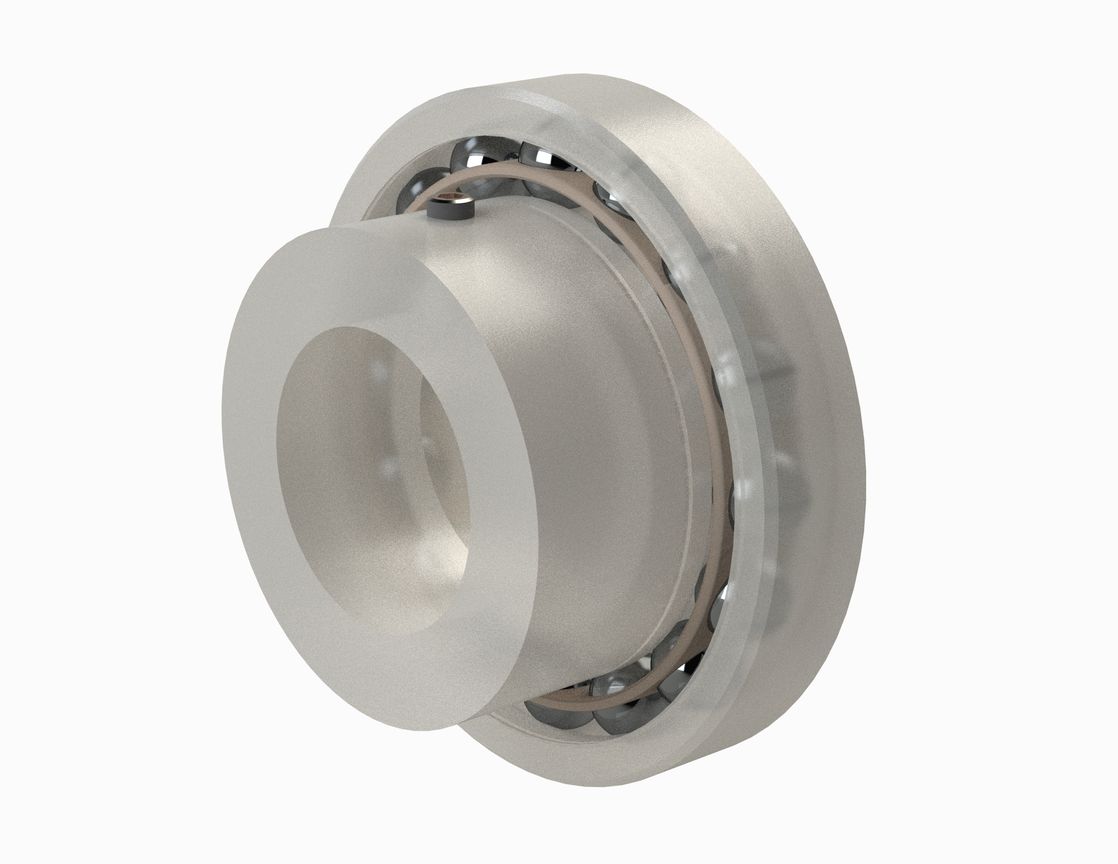
- Polymer inner and outer cage
- Balls made of stainless steel, glass, polymer or other materials
- Polymer separator.
-
Features and Benefits:
- Corrosion resistance
- Chemical resistance
- Self-lubricating (no lubrication required)
- Light weight (80% less than steel)
- Some high temperature applications
- Low coefficient of friction
- Quiet running
- Good damping properties
- Electrical insulating properties
- Integrated functions for special bearings
- Low life cycle costs

Please find below general recommendations for the material selection and use of polymer ball bearings.
Note: Polymer ball bearings are often subject to conditions that cannot be simulated in laboratory testing (temperature, pressure, material tension, interaction with chemicals, design features, etc.). Due to the complexity of these factors, we recommend field testing the selected polymer ball bearing to ensure that it performs under the specified conditions.
Chemical resistance
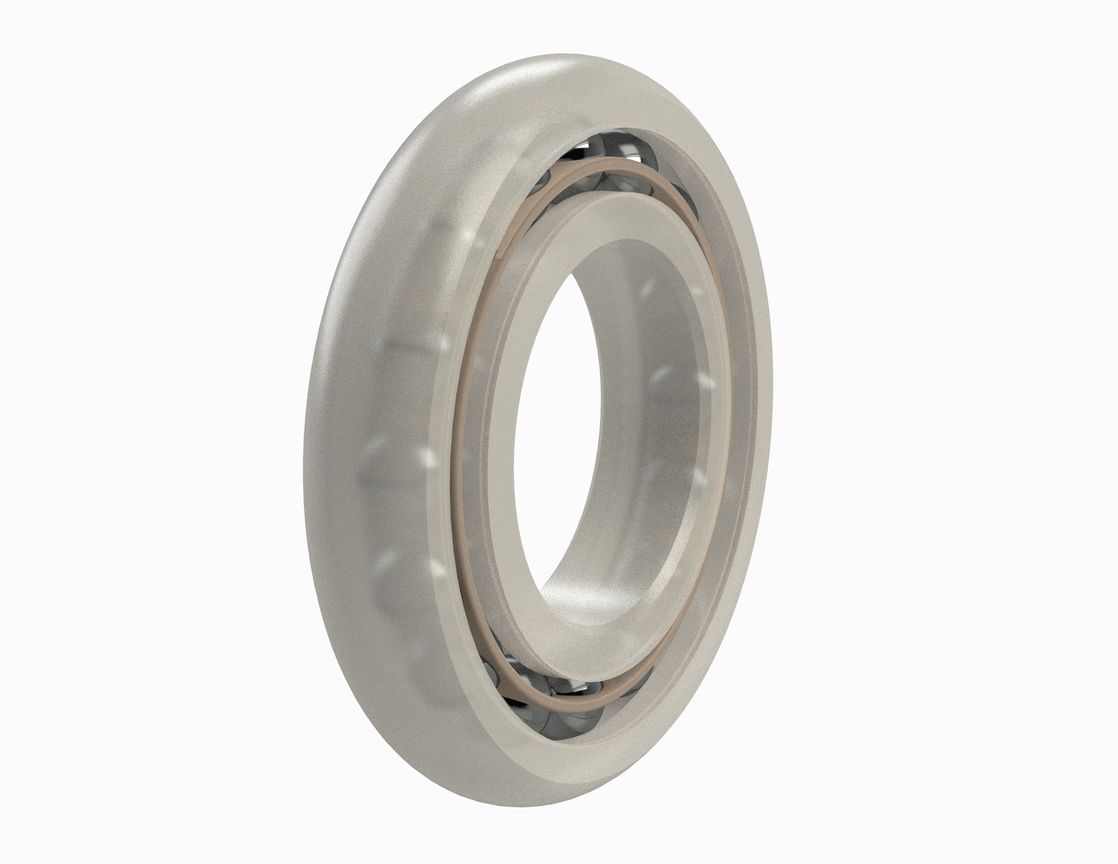

The polymers generally used in the manufacture of ball bearings (polypropylene PP, polyoxymethylene POM, polyamide Pa66) have good chemical resistance. However, depending on the operating conditions, it may be necessary to use alternative polymers that fall outside the standard range.
Polypropylene (PP) is resistant to acids, alkalis, salts and salt solutions, alcohols, oils, greases, waxes and many solvents. Exposure to aromatic compounds and halogenated hydrocarbons leads to swelling. Polypropylene is not resistant to strong oxidising media (e.g. nitric acid, chromates or halogens) and there is a risk of stress cracking corrosion.
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is resistant to weak acids, weak and strong alkalis and organic solvents as well as petrol, benzene, oils and alcohols.
Polyamide 6.6 (PA66) is resistant to almost all common organic solvents as well as some weak acids and alkalis.
Operating temperatures and thermal expansion
Apart from chemical resistance, the key criterion for selecting suitable bearing materials is the operating temperature.
Standard materials can withstand temperatures up to approx. 100 °C. Alternative materials (e.g. PEEK) can withstand temperatures up to 250 °C.
Thermal expansion in conjunction with the operating temperature is also important as the thermal expansion coefficient values of various polymers can be tens of times greater than steel.
Thermal expansion affects the internal clearance of the bearing and must be taken into account when designing the shaft and housing seating.
Load capacity
The load capacity is the ability to support a static load. The ability to support a static load is determined by the upper load limit that the bearing can withstand when stopped without damaging the rolling elements or raceways.
Dynamic load capacity
Due to the current state of technology it is not possible to calculate the service life analytically.
The dynamic load capacity is an indicator for the operating load that enables the bearing to fulfil its function in the majority of cases.
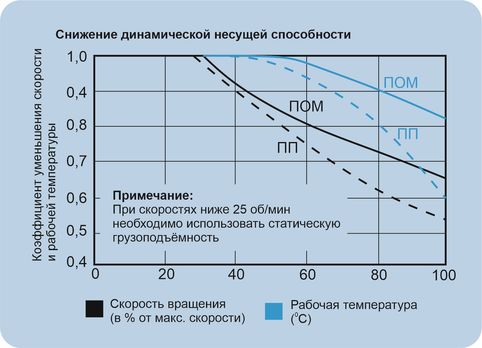
The dynamic load capacity depends on speed and operating temperature. The influence of operating temperature and bearing speed on the dynamic load capacity can be estimated from the diagram below.

 Назад
Назад